An altered chord is a seventh or extended chord in which the fifth note of the chord and/or an extension note — the ninth, 11th or 13th — is altered, either raised or lowered by a half step.
This post will cover how to construct dominant chords with combined alterations and provide examples for each type of chord.
It will also provide common fingerings for each chord, along with instruction on how to play them on a guitar with any root note.
Dominant Seventh, Flat Five, Flat Nine Chords
If we lower the fifth and ninth scale degrees of a dominant ninth chord, it becomes a dominant seventh, flat five, flat nine chord.
The chord formula for a dominant seventh, flat five, flat nine chord is: 1, 3, b5, b7, b9.
A dominant seventh, flat five, flat nine chord contains the first, third, flatted fifth, flatted seventh and flatted ninth degrees of the major scale with the same root note:
- A C7(b5b9) chord contains the notes C, E, Gb, Bb and Db — the first, third, flatted fifth, flatted seventh and flatted ninth notes in a C major scale (fig.1a).
- An A7(b5b9) chord contains the notes A, C#, Eb, G and Bb — the first, third, flatted fifth, flatted seventh and flatted ninth notes in an A major scale (fig.1b).
Fig.1

Dominant Seventh, Sharp Five, Sharp Nine Chords
If we raise the fifth and ninth scale degrees of a dominant ninth chord, it becomes a dominant seventh, sharp five, sharp nine chord.
The chord formula for a dominant seventh, sharp five, sharp nine chord is: 1, 3, #5, b7, #9.
A dominant seventh, sharp five, sharp nine chord contains the first, third, sharped fifth, flatted seventh and sharped ninth degrees of the major scale with the same root note:
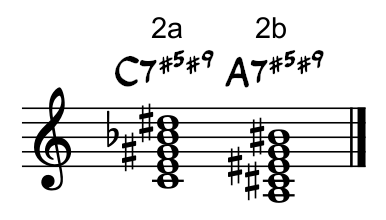
- A C7(#5#9) chord contains the notes C, E, G#, Bb and D# — the first, third, sharped fifth, flatted seventh and sharped ninth notes in a C major scale (fig.2a).
- An A7(#5#9) chord contains the notes A, C#, E#, G and B# — the first, third, sharped fifth, flatted seventh and sharped ninth notes in an A major scale (fig.2b).
Fig.2
Dominant Seventh, Flat Five, Sharp Nine Chords
If we lower the fifth and raise the ninth scale degrees of a dominant ninth chord, it becomes a dominant seventh, flat five, sharp nine chord.
The chord formula for a dominant seventh, flat five, sharp nine chord is: 1, 3, b5, b7, #9.
A dominant seventh flat five, sharp nine chord contains the first, third, flatted fifth, flatted seventh and sharped ninth degrees of the major scale with the same root note:
- A C7(b5#9) chord contains the notes C, E, Gb, Bb and D# — the first, third, flatted fifth, flatted seventh and sharped ninth notes in a C major scale (fig.3a).
- An A7(b5#9) chord contains the notes A, C#, Eb, G and B# — the first, third, flatted fifth, flatted seventh and sharped ninth notes in an A major scale (fig.3b).
Fig.3
Dominant Seventh, Sharp Five, Flat Nine Chords
If we raise the fifth and lower the ninth scale degrees of a dominant ninth chord, it becomes a dominant seventh, sharp five, flat nine chord.
The chord formula for a dominant seventh, sharp five, flat nine chord is: 1, 3, #5, b7, b9.
A dominant seventh sharp five, flat nine chord contains the first, third, sharped fifth, flatted seventh and flatted ninth degrees of the major scale with the same root note:
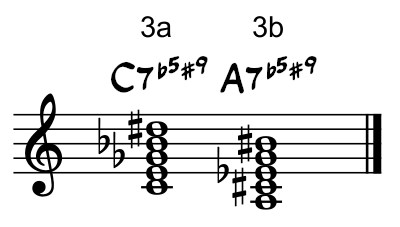
- A C7(#5b9) chord contains the notes C, E, G#, Bb and Db — the first, third, sharped fifth, flatted seventh and flatted ninth notes in a C major scale (fig.4a).
- An A7(#5b9) chord contains the notes A, C#, E#, G and Bb — the first, third, sharped fifth, flatted seventh and flatted ninth notes in an A major scale (fig.4b).
Fig.4

Summary of Altered Dominant Chord Formulas
The altered dominant chord formulas covered in this post are summarized below:
- Dominant seventh, flat five, flat nine: 1, 3, b5, b7, b9.
- Dominant seventh, sharp five, sharp nine: 1, 3, #5, b7, #9.
- Dominant seventh, flat five, sharp nine: 1, 3, b5, b7, #9.
- Dominant seventh, sharp five, flat nine: 1, 3, #5, b7, b9.
Omitted Notes
All of the notes in an altered chord formula don’t necessarily have to be included in any particular chord voicing. Some notes are less important than others and can be omitted.
The important notes that should always be included in an altered chord voicing are the chord’s third and seventh degrees, the highest extension note and any altered notes.
Root notes, the fifth scale degree and other extension notes are routinely left out of altered chord voicings on a guitar.
Altered Dominant Chords on a Guitar
Common fingerings and examples for the altered dominant chords covered in the post are provided below.
Dominant Seventh, Flat Five, Flat Nine Chords
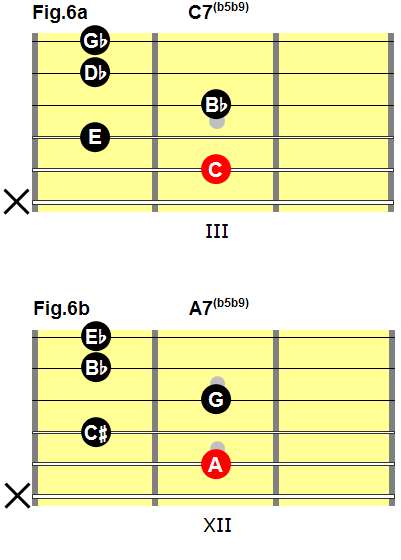
Fig.5 shows a common fingering for a dominant seventh, flat five, flat nine chord.
Fig.5

This fingering will allow you to play a dominant seventh, flat five, flat nine chord with any root note:
- To play a C7(b5b9) chord, place the barre on the second fret (fig.6a).
- To play an A7(b5b9) chord, place the barre on the 11th fret (fig.6b).
Fig.6
Dominant Seventh, Sharp Five, Sharp Nine Chords
Fig.7 shows a common fingering for a dominant seventh, sharp five, sharp nine chord.
Fig.7
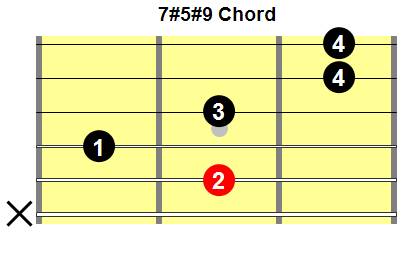
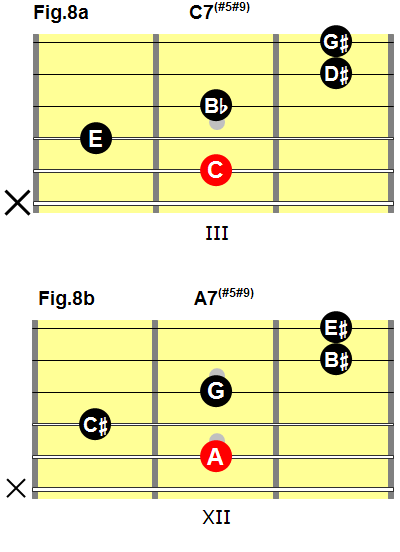
This fingering will allow you to play a dominant seventh, sharp five, sharp nine chord with any root note:
- To play a C7(#5#9) chord, place your second finger on the C on the fifth string, third fret (fig.8a).
- To play an A7(#5#9) chord, place your second finger on the A on the fifth string, 12th fret (fig.8b).
Fig.8
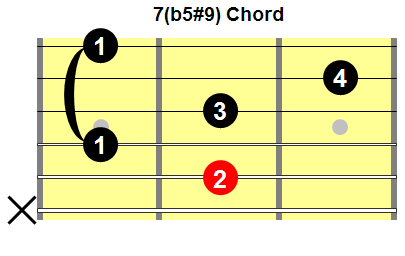
Dominant Seventh, Flat Five, Sharp Nine Chord
Fig.9 shows a common fingering for a dominant seventh, flat five, sharp nine chord.
Fig.9
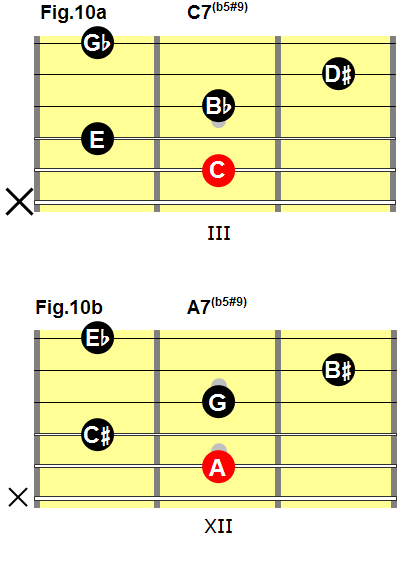
This fingering will allow you to play a dominant seventh, flat five, sharp nine chord with any root note:
- To play a C7(b5#9) chord, place the barre on the second fret (fig.10a).
- To play an A7(b5#9) chord, place the barre on the 11th fret (fig.10b).
Fig.10
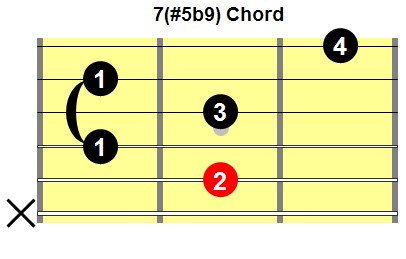
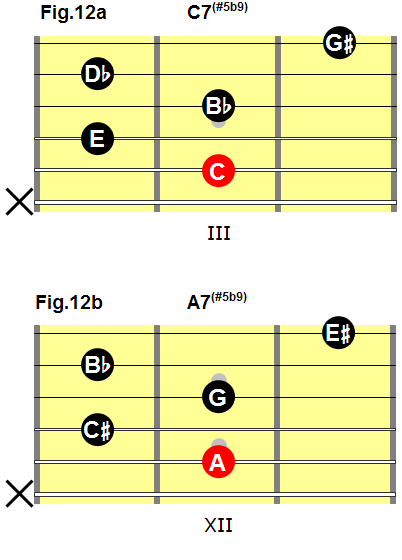
Dominant Seventh, Flat Five, Sharp Nine Chords
Fig.11 shows a common fingering for a dominant seventh, flat five, sharp nine chord.
Fig.11
This fingering will allow you to play a dominant seventh, sharp five, flat nine chord with any root note:
- To play a C7(#5b9) chord, place the barre on the second fret (fig.12a).
- To play an A7(#5b9) chord, place the barre on the 11th fret (fig.12b).
Fig.12
Chord Substitutions
It’s common in jazz and other forms of music for a player to substitute an altered dominant chord for an unaltered dominant chord presented in the music.
The altered note or notes will serve to color the chord and create greater dissonance within it.
Related Posts
Related posts include:
- Extended Chords I: Ninth Chords.
- Altered Dominant Chords I: Single Alterations.
- Creating Chord Voicings I.
- Creating Chord Voicings II.
- The Dominant Diminished Scale.
- Soloing Over Altered Dominant Chords.
